ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION
 | |
| A 50 kVA pole-mounted distribution transformer |
Electric electricity distribution is the final level inside the delivery of electrical energy; it consists of energy from the transmission system to individual customers. Distribution substations hook up with the transmission gadget and lower the transmission voltage to medium voltage ranging between 2 kV and 35 kV with the use of transformers. Primary distribution strains carry this medium voltage energy to distribution transformers placed close to the client's premises. Distribution transformers again decrease the voltage to the usage voltage used by lights, industrial gadget and household home equipment. Often numerous customers are furnished from one transformer thru secondary distribution strains. Commercial and residential customers are related to the secondary distribution strains thru service drops. Customers disturbing a miles large quantity of electricity can be related at once to the number one distribution degree or the subtransmission level.
The transition from transmission to distribution occurs in a strength substation, which has the subsequent functions:
* Circuit breakers and switches enable the substation to be disconnected from the transmission grid or for distribution traces to be disconnected.
* Transformers step down transmission voltages, 35 kV or extra, right down to primary distribution voltages. These are medium voltage circuits, typically six hundred–35000 V.
* From the transformer, strength goes to the busbar that could cut up the distribution strength off in multiple guidelines. The bus distributes electricity to distribution strains, which fan out to customers.
Urban distribution is in particular underground, on occasion in not common utility ducts. Rural distribution is on the whole above floor with utility poles, and suburban distribution is a combination. Closer to the purchaser, a distribution transformer steps the number one distribution energy all the way down to a low-voltage secondary circuit, typically one hundred twenty/240 V inside the US for residential customers. The electricity comes to the purchaser via a service drop and an electricity meter. The final circuit in an city device can be less than 15 metres (50 toes), but may be over ninety one metres (three hundred toes) for a rural consumer.
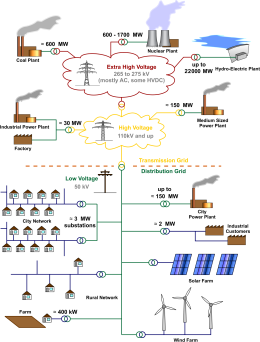 |
| General layout of electricity networks. the voltages and loadings are typical of a European network. |
History
 |
| The l;ate 1870s and early 1880s saw the introduction of arc lamp lighting used outdoor or in large indoor spaces such as this Brush Electric Company system instlled in 1880 in New York City. |
Electric energy distribution have become necessary only within the Eighties whilst strength started out being generated at power stations. Before that power became typically generated where it become used. The first strength distribution structures hooked up in European and US cities had been used to deliver lighting: arc lights running on very excessive voltage (round 3000 volts) alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC), and incandescent lighting fixtures jogging on low voltage (one hundred volt) direct cutting-edge. Both were supplanting gas lights structures, with arc lights taking over huge area and street lighting, and incandescent lighting replacing gasoline for enterprise and residential lights.
Due to the excessive voltages utilized in arc lights, a single producing station ought to deliver a long string of lights, up to 7-mile (11 km) lengthy circuits. Each doubling of the voltage would permit the same size cable to transmit the same quantity of strength 4 times the gap for a given electricity loss. Direct cutting-edge indoor incandescent lights structures, for instance the primary Edison Pearl Street Pearl StreetStation mounted in 1882, had problem presenting clients more than a mile away. This turned into due to the low one hundred ten volt system getting used at some stage in the gadget, from the turbines to the very last use. The Edison DC machine wished thick copper conductor cables, and the producing plant life needed to be inside approximately 1.5 miles (2.4 km) of the farthest purchaser to avoid excessively huge and costly conductors.
Introduction of the transformer
Transmitting power an extended distance at high voltage after which decreasing it to a decrease voltage for lights have become a recognized engineering roadblock to electric powered electricity distribution with many, no longer very pleasant, solutions tested by using lights agencies. The mid-1880s saw a step forward with the improvement of useful transformers that allowed the AC voltage to be "stepped up" to a great deal better transmission voltages and then dropped down to a lower cease person voltage. With a great deal cheaper transmission expenses and the greater economies of scale of having massive producing plant life deliver complete towns and areas, using AC spread hastily.
In america the competition between direct contemporary and alternating cutting-edge took a private turn within the late Eighties within the form of a "war of currents" when Thomas Edison started attacking George Westinghouse and his improvement of the primary US AC transformer systems, stating all of the deaths due to high-voltage AC structures through the years and claiming any AC device changed into inherently dangerous. Edison's propaganda marketing campaign changed into brief-lived, with his employer switching over to AC in 1892.
AC became the dominant form of transmission of electricity with innovations in Europe and the USA in electric powered motor designs and the improvement of engineered accepted structures allowing the big range of legacy structures to be connected to big AC grids.
In the primary half of the 20 th century, in lots of locations the electrical power industry become vertically integrated, that means that one employer did technology, transmission, distribution, metering and billing. Starting in the Seventies and 1980s, international locations began the procedure of deregulation and privatisation, leading to electricity markets. The distribution device could remain regulated, however era, retail, and sometimes transmission systems were transformed into competitive markets.
Generation and transmission
 |
| Simplified diagram of AC electricity delivery from generation station to consumers' service drop. |
Electric electricity begins at a generating station, in which the ability distinction may be as excessive as 33,000 volts. AC is generally used. Users of huge quantities of DC electricity along with a few railway electrification systems, telephone exchanges and industrial processes inclusive of aluminium smelting use rectifiers to derive DC from the general public AC deliver, or may additionally have their very own generation systems. High-voltage DC may be high-quality for isolating alternating-contemporary systems or controlling the quantity of energy transmitted. For instance, Hydro-Québec has an immediate-modern line which goes from the James Bay location to Boston.
From the producing station it goes to the generating station's switchyard in which a step-up transformer increases the voltage to a level appropriate for transmission, from forty four kV to 765 kV. Once inside the transmission machine, energy from every producing station is mixed with energy produced some place else. Electricity is consumed as quickly as it's miles produced. It is transmitted at a completely high pace, close to the speed of light.
Primary Distribution
Primary distribution voltages range from 4 kV to 35 kV section-to-phase (2.4 kV to 20 kV phase-to-impartial)[9] Only large purchasers are fed immediately from distribution voltages; most software clients are connected to a transformer, which reduces the distribution voltage to the low voltage "utilization voltage", "supply voltage" or "mains voltage" used by lighting fixtures and interior wiring structures.
Network configurations
 |
| Substation near Yellowknife , in the Northwest Territories of Canada |
Distribution networks are divided into two kinds, radial or community. A radial device is arranged like a tree wherein every consumer has one supply of supply. A network gadget has more than one sources of deliver working in parallel. Spot networks are used for focused hundreds. Radial systems are commonly used in rural or suburban areas.
Radial systems typically include emergency connections in which the device may be reconfigured in case of troubles, together with a fault or planned upkeep. This can be accomplished with the aid of commencing and closing switches to isolate a sure segment from the grid.
Long feeders revel in voltage drop (power factor distortion) requiring capacitors or voltage regulators to be established.
Reconfiguration, by exchanging the useful links among the elements of the machine, represents one of the maximum vital measures which can improve the operational overall performance of a distribution machine. The problem of optimization thru the reconfiguration of a electricity distribution machine, in terms of its definition, is a historic unmarried objective hassle with constraints. Since 1975, whilst Merlin and Back added the concept of distribution machine reconfiguration for lively strength loss discount, till nowadays, loads of researchers have proposed various strategies and algorithms to remedy the reconfiguration problem as a unmarried goal trouble. Some authors have proposed Pareto optimality based procedures (together with lively strength losses and reliability indices as goals). For this motive, unique artificial intelligence based techniques have been used: microgenetic, department alternate, particle swarm optimization and non-ruled sorting genetic algorithm.
Rural services
Rural electrification systems have a tendency to apply better distribution voltages due to the longer distances protected by means of distribution lines (see Rural Electrification Administration). 7.2, 12.Forty seven, 25, and 34.Five kV distribution is not unusual inside the United States; eleven kV and 33 kV are not unusual in the UK, Australia and New Zealand; eleven kV and 22 kV are commonplace in South Africa; 10, 20 and 35 kV are commonplace in China. Other voltages are every now and then used.
Rural services normally try and decrease the number of poles and wires. It makes use of higher voltages (than city distribution), which in turn permits use of galvanized metallic twine. The strong metallic twine lets in for less high priced wide pole spacing. In rural regions a pole-mount transformer may additionally serve handiest one patron. In New Zealand, Australia, Saskatchewan, Canada, and South Africa, Single-cord earth return systems (SWER) are used to electrify faraway rural areas.
Three segment provider presents energy for big agricultural centers, petroleum pumping centers, water plant life, or different customers that have huge hundreds (Three segment gadget). In North America, overhead distribution structures may be 3 phase, 4 twine, with a impartial conductor. Rural distribution system may also have long runs of 1 phase conductor and a neutral. In other nations or in severe rural areas the impartial twine is attached to the floor to use that as a return (Single-twine earth return). This is referred to as an ungrounded wye device.
Secondary distribution
 |
| World map of mains voltage and frequencies |
A ground connection is commonly furnished for the patron's system in addition to for the gadget owned through the software. The purpose of connecting the customer's gadget to ground is to limit the voltage which can increase if high voltage conductors give way onto lower-voltage conductors which can be generally set up lower to the ground, or if a failure takes place inside a distribution transformer. Earthing systems can be TT, TN-S, TN-C-S or TN-C.
Regional variations
220-240 volt systems
Most of the arena uses 50 Hz 220 or 230 V single section, or 400 V three segment for residential and mild business offerings. In this device, the primary distribution community materials some substations consistent with area, and the 230 V / 400 V power from each substation is without delay allotted to give up users over a vicinity of commonly much less than 1 km radius. Three live (hot) wires and the neutral are related to the constructing for a three segment service. Single-phase distribution, with one live cord and the impartial is used domestically where total hundreds are light. In Europe, electricity is generally disbursed for enterprise and domestic use by way of the three-section, four cord device. This gives a segment-to-phase voltage of four hundred volts wye service and a single-section voltage of 230 volts among anyone section and impartial. In the United Kingdom a regular city or suburban low-voltage substation could typically be rated among a hundred and fifty kVA and 1 MVA and supply a whole neighbourhood of a few hundred houses. Transformers are generally sized on a median load of one to 2 kW according to household, and the carrier fuses and cable is sized to permit someone belongings to draw a top load of perhaps ten times this. For commercial customers, three-segment 690 / four hundred volt is also available, or may be generated domestically. Large business customers have their personal transformer(s) with an enter from 11 kV to 220 kV.
100-120 volt systems
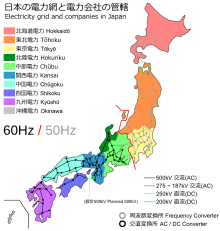 |
| Japan's utility frequencies are 50 Hz and 60 Hz. |
Most of the Americas use 60 Hz AC, the 120/240 volt split-phase system domestically and 3 section for large installations. North American transformers generally power houses at 240 volts, similar to Europe's 230 volts. It is the split-segment that lets in use of 120 volts inside the domestic.
In the electricity sector in Japan, the same old voltage is 100 V, with each 50 and 60 Hz AC frequencies being used. Parts of the u . S . Use 50 Hz, while different parts use 60 Hz. This is a relic from the Eighteen Nineties. Some neighborhood companies in Tokyo imported 50 Hz German system, while the neighborhood strength providers in Osaka brought in 60 Hz generators from america. The grids grew until subsequently the entire usa become stressed out. Today the frequency is 50 Hz in Eastern Japan (along with Tokyo, Yokohama, Tohoku, and Hokkaido) and 60 Hz in Western Japan (which include Nagoya, Osaka, Kyoto, Hiroshima, Shikoku, and Kyushu).
Most family appliances are made to paintings on either frequency. The problem of incompatibility came into the public eye when the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami knocked out about a third of the east's potential, and power in the west couldn't be completely shared with the east, since the united states does not have a common frequency.
There are four high-voltage direct cutting (HVDC) converter stations that circulate strength throughout Japan's AC frequency border. Shin Shinano is a again-to-back HVDC facility in Japan which forms one among four frequency charger stations that link Japan's western and jap energy grids. The different three are at Higashi-Shimizu, Minami-Fukumitsu and Sakuma Dam. Together they could circulate up to 1.2 GW of strength east or west.
240 volt systems and 120 voltoutlets
Most current North American houses are stressed to receive 240 volts from the transformer, and via the usage of split-phase electrical power, may have each one hundred twenty volt receptacles and 240 volt receptacles. The one hundred twenty volts is commonly used for lights and most wall outlets. The 240 volt circuits are commonly used for home equipment requiring high watt heat output including ovens and warmers. They will also be used to deliver an electric car charger.
Modern Distribution Systems
Traditionally, the distribution structures could only function as simple distribution traces in which the strength from the transmission networks could be shared some of the customers. Today's distribution structures are closely incorporated with renewable energy generations at the distribution degree of the electricity structures via the way of distributed generation sources, inclusive of solar energy and wind energy.As a result, distribution systems have become extra impartial from the transmission networks day-by using-day. Balancing the supply-call for relationship at those modern-day distribution networks (occasionally known as microgrids) is extraordinarily difficult, and it requires the usage of numerous technological and operational approach to operate. Such gear consist of battery storage power station, records analytics, optimization gear, and many others.
WRITTEN BY : ADRISH WAHEED
Labels: ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home