EARTHQUAKE
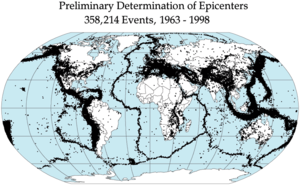 |
| Earthquake epicenters arise basically along tectonic plate obstacles, and especially on the Pacific Ring of Fire. |
An earthquake (also referred to as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a unexpected launch of electricity in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in length from those which are so weak that they can't be felt to those violent enough to propel gadgets and those into the air, and wreak destruction across complete towns. The seismicity, or seismic hobby, of a place is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes skilled over a specific time period. The phrase tremor is likewise used for non-earthquake seismic rumbling.
 |
| Global plate tectonic movement |
At the Earth's floor, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a big earthquake is placed offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to purpose a tsunami. Earthquakes can also cause landslides and, on occasion, volcanic interest.
In its maximum general sense, the word earthquake is used to describe any seismic event—whether or not natural or due to humans—that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes are induced mostly through rupture of geological faults but also by other activities which include volcanic pastime, landslides, mine blasts, and nuclear tests. An earthquake's point of preliminary rupture is called its hypocenter or focus. The epicenter is the factor at floor stage directly above the hypocenter.
Naturally occuring earthquakes
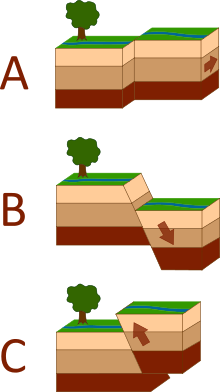 | ||||
| Three types of faults : A . Strike-slip | B. Normal C. Reverse |
Tectonic earthquakes arise everywhere within the earth where there's sufficient stored elastic stress energy to force fracture propagation along a fault aircraft. The sides of a fault circulate past every other easily and aseismically best if there are no irregularities or asperities along the fault floor that growth the frictional resistance. Most fault surfaces do have such asperities, which ends up in a form of stick-slip behavior. Once the fault has locked, continued relative motion among the plates leads to growing strain and, therefore, saved strain strength within the extent across the fault surface. This maintains till the strain has risen sufficiently to interrupt through the asperity, suddenly allowing sliding over the locked part of the fault, releasing the saved strength. This power is launched as a combination of radiated elastic stress seismic waves, frictional heating of the fault surface, and cracking of the rock, for this reason causing an earthquake. This technique of slow construct-up of stress and pressure punctuated by using occasional unexpected earthquake failure is known as the elastic-rebound theory. It is estimated that simplest 10 percentage or much less of an earthquake's total energy is radiated as seismic electricity. Most of the earthquake's energy is used to energy the earthquake fracture growth or is converted into warmth generated through friction. Therefore, earthquakes decrease the Earth's available elastic potential energy and raise its temperature, although those changes are negligible in comparison to the conductive and convective float of warmth out from the Earth's deep interior.
Earthquake fault types
There are three foremost forms of fault, all of which may also reason an interplate earthquake: regular, opposite (thrust), and strike-slip. Normal and opposite faulting are examples of dip-slip, in which the displacement along the fault is inside the course of dip and where motion on them includes a vertical element. Normal faults arise specially in areas in which the crust is being prolonged consisting of a divergent boundary. Reverse faults arise in areas in which the crust is being shortened along with at a convergent boundary. Strike-slip faults are steep systems in which the 2 aspects of the fault slip horizontally past each different; remodel obstacles are a selected form of strike-slip fault. Many earthquakes are resulting from movement on faults which have additives of both dip-slip and strike-slip; that is known as oblique slip.
Reverse faults, especially those along convergent plate limitations, are related to the maximum effective earthquakes, megathrust earthquakes, which include almost all of these of importance eight or extra. Megathrust earthquakes are accountable for approximately ninety% of the entire seismic second launched worldwide. Strike-slip faults, mainly continental transforms, can produce primary earthquakes as much as about value eight. Earthquakes associated with normal faults are typically much less than significance 7. For each unit boom in value, there's a more or less thirtyfold increase inside the electricity launched. For example, an earthquake of value 6.0 releases approximately 32 times extra electricity than a five.Zero magnitude earthquake and a 7.0 importance earthquake releases 1,000 times greater energy than a 5.0 importance earthquake. An eight.6 importance earthquake releases the same amount of power as 10,000 atomic bombs of the scale used in World War II.
This is so because the strength released in an earthquake, and accordingly its importance, is proportional to the vicinity of the fault that ruptures and the stress drop. Therefore, the longer the length and the wider the width of the faulted place, the larger the ensuing value. The topmost, brittle a part of the Earth's crust, and the cool slabs of the tectonic plates which can be descending into the hot mantle, are the only components of our planet which could keep elastic electricity and release it in fault ruptures. Rocks warmer than about 300 °C (572 °F) drift in response to pressure; they do no longer rupture in earthquakes. The most discovered lengths of ruptures and mapped faults (which may also smash in a unmarried rupture) are approximately 1,000 km (620 mi). Examples are the earthquakes in Alaska (1957), Chile (1960), and Sumatra (2004), all in subduction zones. The longest earthquake ruptures on strike-slip faults, like the San Andreas Fault (1857, 1906), the North Anatolian Fault in Turkey (1939), and the Denali Fault in Alaska (2002), are about 1/2 to one 0.33 so long as the lengths alongside subducting plate margins, and those along regular faults are even shorter.
 |
| Aerial image of the San Andreas Fault inside the Carrizo Plain, northwest of Los Angeles |
The maximum vital parameter controlling the maximum earthquake significance on a fault, however, isn't always the most to be had period, but the to be had width because the latter varies by way of a issue of 20. Along converging plate margins, the dip attitude of the rupture plane could be very shallow, typically approximately 10 degrees. Thus, the width of the aircraft in the pinnacle brittle crust of the Earth can end up 50–one hundred km (31–62 mi) (Japan, 2011; Alaska, 1964), making the maximum effective earthquakes feasible.
Strike-slip faults tend to be orientated close to vertically, resulting in an approximate width of 10 km (6.2 mi) inside the brittle crust. Thus, earthquakes with magnitudes an awful lot larger than 8 are not viable. Maximum magnitudes alongside many regular faults are even more restricted due to the fact many of them are placed alongside spreading centers, as in Iceland, where the thickness of the brittle layer is simplest approximately six kilometres (3.7 mi).
In addition, there exists a hierarchy of pressure levels within the three fault types. Thrust faults are generated by way of the best, strike-slip by means of intermediate, and everyday faults by the bottom stress levels. This can without difficulty be understood by way of thinking about the path of the best predominant stress, the path of the force that "pushes" the rock mass in the course of the faulting. In the case of ordinary faults, the rock mass is driven down in a vertical path, thus the pushing pressure (best predominant strain) equals the load of the rock mass itself. In the case of thrusting, the rock mass "escapes" inside the course of the least primary strain, specifically upward, lifting the rock mass, and consequently, the overburden equals the least primary pressure. Strike-slip faulting is intermediate among the opposite sorts described above. This distinction in pressure regime inside the 3 faulting environments can contribute to variations in stress drop at some point of faulting, which contributes to variations inside the radiated power, no matter fault dimensions.
Earthquakes away from plate boundries
 |
| Comparison of the 1985 and 2017 earthquakes on Mexico City, Puebla and Michoacán/Guerrero |
Where plate barriers occur within the continental lithosphere, deformation is spread out over a miles larger area than the plate boundary itself. In the case of the San Andreas fault continental remodel, many earthquakes occur away from the plate boundary and are associated with traces advanced inside the broader area of deformation as a result of main irregularities within the fault trace (e.G., the "Big bend" area). The Northridge earthquake turned into related to motion on a blind thrust within this type of sector. Another instance is the strongly oblique convergent plate boundary between the Arabian and Eurasian plates in which it runs through the northwestern a part of the Zagros Mountains. The deformation associated with this plate boundary is partitioned into almost pure thrust feel movements perpendicular to the boundary over a huge region to the southwest and almost natural strike-slip motion alongside the Main Recent Fault close to the real plate boundary itself. This is demonstrated by earthquake focal mechanisms.
All tectonic plates have inner strain fields caused by their interactions with neighboring plates and sedimentary loading or unloading (e.G., deglaciation). These stresses can be sufficient to motive failure alongside current fault planes, giving rise to intraplate earthquakes.
Shallow-focus and deep-focus earthquakes
 |
| Collapsed Gran Hotel constructing inside the San Salvador city, after the shallow 1986 San Salvador earthquake |
The majority of tectonic earthquakes originate inside the ring of fireplace at depths not exceeding tens of kilometers. Earthquakes taking place at a intensity of much less than 70 km (forty three mi) are labeled as "shallow-recognition" earthquakes, even as people with a focal-intensity among 70 and three hundred km (forty three and 186 mi) are typically termed "mid-awareness" or "intermediate-intensity" earthquakes. In Subduction zones, where older and less warm oceanic crust descends underneath any other tectonic plate, deep-focus earthquakes may also arise at much extra depths (ranging from 300 to 700 km (a hundred ninety to 430 mi)). These seismically active regions of subduction are called Wadati–Benioff zones. Deep-recognition earthquakes occur at a intensity where the subducted lithosphere should now not be brittle, because of the high temperature and pressure. A possible mechanism for the generation of deep-awareness earthquakes is faulting due to olivine present process a phase transition right into a spinel structure.
Earthquake and volcanic activity
Earthquakes often arise in volcanic areas and are brought about there, each by means of tectonic faults and the motion of magma in volcanoes. Such earthquakes can function an early caution of volcanic eruptions, as at some point of the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens. Earthquake swarms can function markers for the location of the flowing magma for the duration of the volcanoes. These swarms can be recorded via seismometers and tiltmeters (a tool that measures floor slope) and used as sensors to predict coming near near or upcoming eruptions.
Rupture dynamics
A tectonic earthquake starts through an preliminary rupture at a point at the fault surface, a method referred to as nucleation. The scale of the nucleation area is unsure, with a few proof, including the rupture dimensions of the smallest earthquakes, suggesting that it's far smaller than one hundred m (330 feet) whilst other evidence, which includes a slow aspect discovered by using low-frequency spectra of a few earthquakes, advise that it's far large. The opportunity that the nucleation entails some sort of preparation manner is supported with the aid of the statement that about 40% of earthquakes are preceded by way of foreshocks. Once the rupture has initiated, it begins to propagate alongside the fault floor. The mechanics of this procedure are poorly understood, partially because it is difficult to recreate the excessive sliding velocities in a laboratory. Also, the results of strong ground movement make it very tough to file statistics close to a nucleation zone.
Rupture propagation is generally modeled the usage of a fracture mechanics method, likening the rupture to a propagating blended mode shear crack. The rupture pace is a feature of the fracture energy within the quantity across the crack tip, increasing with decreasing fracture energy. The speed of rupture propagation is orders of magnitude quicker than the displacement pace across the fault. Earthquake ruptures commonly propagate at velocities which might be in the variety 70–90% of the S-wave pace, that's impartial of earthquake length. A small subset of earthquake ruptures seem to have propagated at speeds more than the S-wave speed. These supershear earthquakes have all been discovered for the duration of massive strike-slip activities. The unusually wide region of coseismic harm due to the 2001 Kunlun earthquake has been attributed to the results of the sonic boom advanced in such earthquakes. Some earthquake ruptures journey at strangely low velocities and are known as sluggish earthquakes. A specifically risky shape of gradual earthquake is the tsunami earthquake, discovered wherein the exceptionally low felt intensities, as a result of the slow propagation speed of a few great earthquakes, fail to alert the population of the neighboring coast, as in the 1896 Sanriku earthquake.
Co-seismic overpressuring and effect of pore pressure
During an earthquake, high temperatures can increase at the fault plane so growing pore strain consequently to vaporization of the floor water already contained inside rock. In the coseismic segment, such increase can notably have an effect on slip evolution and pace and, moreover, within the post-seismic phase it can manipulate the Aftershock collection due to the fact, after the principle occasion, pore stress increase slowly propagates into the surrounding fracture community. From the factor of view of the Mohr-Coulomb energy principle, an boom in fluid pressure reduces the regular stress acting at the fault plane that holds it in area, and fluids can exert a lubricating effect. As thermal overpressurization may also provide tremendous remarks between slip and power fall at the fault aircraft, a commonplace opinion is that it could decorate the faulting manner instability. After the mainshock, the stress gradient among the fault aircraft and the neighboring rock reasons a fluid flow which increases pore stress inside the surrounding fracture networks; such boom may trigger new faulting techniques by using reactivating adjoining faults, giving rise to aftershocks. Analogously, synthetic pore stress boom, by using fluid injection in Earth’s crust, may also set off seismicity.
Tidal force
Tides may induce some seismicity .
Earthquake clusters
Most earthquakes form part of a chain, related to each different in phrases of region and time. Most earthquake clusters include small tremors that cause little to no damage, but there is a theory that earthquakes can recur in a ordinary sample.
Aftershocks
 |
| Magnitude of the Central Italy earthquakes of August and October 2016 and January 2017 and the aftershocks (which endured to arise after the length proven right here) |
An aftershock is an earthquake that happens after a preceding earthquake, the mainshock. Rapid changes of strain between rocks, and the strain from the authentic earthquake are the primary causes of these aftershocks, together with the crust around the ruptured fault plane as it adjusts to the consequences of the mainshock. An aftershock is in the identical location of the primary shock however continually of a smaller importance, but they can nevertheless be powerful enough to motive even greater damage to buildings that were already previously damaged from the authentic quake. If an aftershock is larger than the mainshock, the aftershock is redesignated as the mainshock and the unique important surprise is redesignated as a foreshock. Aftershocks are shaped because the crust around the displaced fault plane adjusts to the consequences of the mainshock.
Earthquake swarms
Earthquake swarms are sequences of earthquakes striking in a particular region inside a brief length. They are exceptional from earthquakes observed via a chain of aftershocks with the aid of the fact that no unmarried earthquake in the collection is manifestly the main shock, so none has a first rate higher magnitude than any other. An instance of an earthquake swarm is the 2004 activity at Yellowstone National Park. In August 2012, a swarm of earthquakes shook Southern California's Imperial Valley, showing the most recorded pastime in the location for the reason that 1970s.
Sometimes a chain of earthquakes arise in what has been known as an earthquake storm, in which the earthquakes strike a fault in clusters, every brought about by using the shaking or strain redistribution of the previous earthquakes. Similar to aftershocks however on adjoining segments of fault, these storms arise over the direction of years, and with a number of the later earthquakes as unfavourable as the early ones. Such a sample changed into discovered within the collection of about a dozen earthquakes that struck the North Anatolian Fault in Turkey inside the 20th century and has been inferred for older anomalous clusters of massive earthquakes inside the Middle East.
Intensity of earth quaking and magnitude of earthquakes
Quaking or shaking of the earth is a commonplace phenomenon surely regarded to humans from the earliest times. Before the development of strong-motion accelerometers that may degree peak floor pace and acceleration directly, the depth of the earth-shaking turned into expected based totally at the discovered outcomes, as categorised on numerous seismic intensity scales. Only in the last century has the source of such shaking been diagnosed as ruptures within the Earth's crust, with the intensity of shaking at any locality dependent now not best on the neighborhood ground conditions but also at the energy or significance of the rupture, and on its distance.
The first scale for measuring earthquake magnitudes became developed by means of Charles F. Richter in 1935. Subsequent scales (see seismic value scales) have retained a key feature, in which each unit represents a ten-fold distinction in the amplitude of the floor shaking and a 32-fold difference in power. Subsequent scales also are adjusted to have about the identical numeric value in the limits of the dimensions.
Although the mass media typically reviews earthquake magnitudes as "Richter significance" or "Richter scale", wellknown practice through most seismological government is to specific an earthquake's power on the moment magnitude scale, that is primarily based on the real strength launched through an earthquake.
Frequency of occurrence
It is estimated that around 500,000 earthquakes arise every year, detectable with current instrumentation. About a hundred,000 of those may be felt. Minor earthquakes arise almost constantly round the sector in locations like California and Alaska inside the U.S., as well as in El Salvador, Mexico, Guatemala, Chile, Peru, Indonesia, the Philippines, Iran, Pakistan, the Azores in Portugal, Turkey, New Zealand, Greece, Italy, India, Nepal and Japan. Larger earthquakes occur less regularly, the relationship being exponential; as an instance, more or less ten instances as many earthquakes larger than importance 4 occur in a selected time period than earthquakes larger than magnitude 5. In the (low seismicity) United Kingdom, for instance, it has been calculated that the average recurrences are: an earthquake of three.7–4.6 every year, an earthquake of four.7–5.Five every 10 years, and an earthquake of 5.6 or larger each a hundred years. This is an example of the Gutenberg–Richter regulation.
 |
| The Messina earthquake and tsunami took as many as 2 hundred,000 lives on December 28, 1908, in Sicily and Calabria. |
The wide variety of seismic stations has improved from approximately 350 in 1931 to many hundreds these days. As a end result, many more earthquakes are suggested than within the beyond, but this is because of the enormous improvement in instrumentation, in preference to an growth inside the wide variety of earthquakes. The United States Geological Survey estimates that, seeing that 1900, there were an average of 18 predominant earthquakes (importance 7.0–7.Nine) and one superb earthquake (magnitude eight.Zero or more) consistent with yr, and that this common has been distinctly solid. In current years, the quantity of predominant earthquakes consistent with 12 months has reduced, even though this is probably a statistical fluctuation rather than a systematic trend. More detailed data on the size and frequency of earthquakes is to be had from the USA Geological Survey (USGS). A recent increase within the quantity of principal earthquakes has been cited, which can be defined by means of a cyclical sample of intervals of severe tectonic interest, interspersed with longer intervals of low depth. However, accurate recordings of earthquakes handiest started within the early 1900s, so it is too early to categorically state that that is the case.
Most of the sector's earthquakes (90%, and eighty one% of the largest) take area in the 40,000-kilometre-long (25,000 mi), horseshoe-fashioned quarter called the circum-Pacific seismic belt, known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, which for the maximum part bounds the Pacific Plate. Massive earthquakes have a tendency to occur alongside other plate obstacles too, including alongside the Himalayan Mountains.
With the fast boom of mega-cities which include Mexico City, Tokyo and Tehran in regions of high seismic threat, a few seismologists are warning that a unmarried quake might also claim the lives of up to a few million humans .
Induced seismicity
While maximum earthquakes are resulting from movement of the Earth's tectonic plates, human pastime can also produce earthquakes. Activities both above ground and beneath can also change the stresses and strains on the crust, which include building reservoirs, extracting resources together with coal or oil, and injecting fluids underground for waste disposal or fracking. Most of these earthquakes have small magnitudes. The five.7 significance 2011 Oklahoma earthquake is concept to had been because of disposing wastewater from oil manufacturing into injection wells, and studies factor to the country's oil enterprise because the purpose of different earthquakes within the beyond century. A Columbia University paper suggested that the 8.0 value 2008 Sichuan earthquake turned into prompted through loading from the Zipingpu Dam, though the hyperlink has not been conclusively proved .
WRITTEN BY : ADRISH WAHEED
Labels: EARTHQUAKE

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home